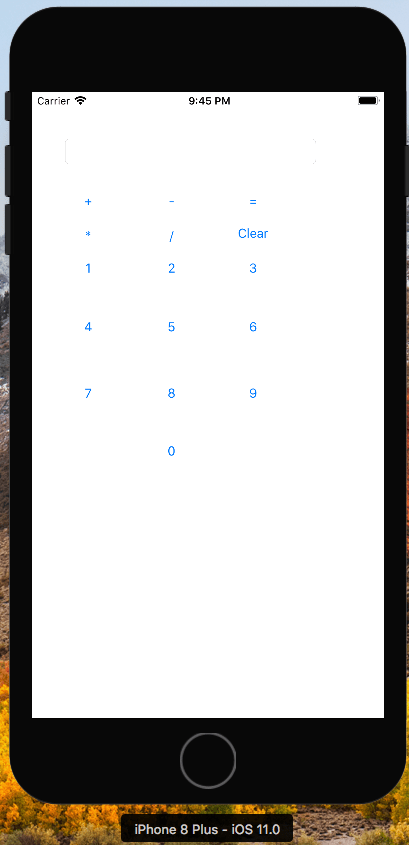
In this video it shows the steps to create a very simple calculator App for iOS. It uses xcode to develop the App. It uses swift language to create the App in very simple steps.
To create the calculator application, it creates a very simple layout using button from 0 to 9 and then basic 4 operators namely: plus, minus, multiplication and division. It create equal to button and clear button to update the results in the text field respectively.
It then create respective IBAction for each of these buttons. IBOutlet for the text field which is used to display the results in the calculator.
I hope you like this video. For any questions, suggestions or appreciation please contact us at: https://programmerworld.co/contact/ or email at: programmerworld1990@gmail.com
Source Code
//
// ViewController.swift
// Simple Calculator
//
// Created by HomePC on 14/10/20.
// Copyright © 2020 HomePC. All rights reserved.
//
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var uiTextFieldResult: UITextField!
var varNumber1 = 0
var varNumber2 = 0
var varNumberResult = 0
var varOperator = "+"
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@IBAction func button1(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "1"
}
@IBAction func button2(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "2"
}
@IBAction func button3(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "3"
}
@IBAction func button4(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "4"
}
@IBAction func button5(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "5"
}
@IBAction func button6(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "6"
}
@IBAction func button7(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "7"
}
@IBAction func button8(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "8"
}
@IBAction func button9(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "9"
}
@IBAction func button0(Sender: UIButton){
uiTextFieldResult.text = uiTextFieldResult.text! + "0"
}
@IBAction func buttonPlus(Sender: UIButton){
varOperator = "+"
varNumber1 = Int(uiTextFieldResult.text!)!
clearText()
}
@IBAction func buttonMinus(Sender: UIButton){
varOperator = "-"
varNumber1 = Int(uiTextFieldResult.text!)!
clearText()
}
@IBAction func buttonMultiplication(Sender: UIButton){
varOperator = "*"
varNumber1 = Int(uiTextFieldResult.text!)!
clearText()
}
@IBAction func buttonDivision(Sender: UIButton){
varOperator = "/"
varNumber1 = Int(uiTextFieldResult.text!)!
clearText()
}
@IBAction func buttonEqual(Sender: UIButton){
varNumber2 = Int(uiTextFieldResult.text!)!
switch varOperator {
case "+":
varNumberResult = varNumber1+varNumber2
uiTextFieldResult.text = String(varNumberResult)
case "-":
varNumberResult = varNumber1-varNumber2
uiTextFieldResult.text = String(varNumberResult)
case "*":
varNumberResult = varNumber1*varNumber2
uiTextFieldResult.text = String(varNumberResult)
case "/":
varNumberResult = varNumber1/varNumber2
uiTextFieldResult.text = String(varNumberResult)
default:
uiTextFieldResult.text = "ERROR"
}
}
@IBAction func buttonClear(Sender: UIButton){
clearText()
}
func clearText() {
uiTextFieldResult.text = ""
}
}
//
// AppDelegate.swift
// Simple Calculator
//
// Created by HomePC on 14/10/20.
// Copyright © 2020 HomePC. All rights reserved.
//
import UIKit
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
return true
}
func applicationWillResignActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Sent when the application is about to move from active to inactive state. This can occur for certain types of temporary interruptions (such as an incoming phone call or SMS message) or when the user quits the application and it begins the transition to the background state.
// Use this method to pause ongoing tasks, disable timers, and invalidate graphics rendering callbacks. Games should use this method to pause the game.
}
func applicationDidEnterBackground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Use this method to release shared resources, save user data, invalidate timers, and store enough application state information to restore your application to its current state in case it is terminated later.
// If your application supports background execution, this method is called instead of applicationWillTerminate: when the user quits.
}
func applicationWillEnterForeground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Called as part of the transition from the background to the active state; here you can undo many of the changes made on entering the background.
}
func applicationDidBecomeActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Restart any tasks that were paused (or not yet started) while the application was inactive. If the application was previously in the background, optionally refresh the user interface.
}
func applicationWillTerminate(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if appropriate. See also applicationDidEnterBackground:.
}
}